Ultimate Guide to Baidu SEO

Baidu is the undisputed leader in China search. To be truly successful in China SEO, you’ll need a deep understanding of how to optimize for the search giant.
However, optimizing for Baidu using the same approach used for Google is unlikely to find your site ranking near the top of page 1. Baidu SEO comes with its own unique and challenging environment of complex language issues, cultural differences, user behavior, legal issues, censorship, and technical considerations.
While the internet is full of guides on how to do SEO for Google, few resources exist in English (or Chinese for that matter) for Baidu SEO. What guides do exist are generally superficial and merely cover the basics. That’s why we’ve created the definitive guide to Baidu SEO to share with the world the expertise we’ve curated through years of developing SEO tools for both global and Asian markets.
This massive, in-depth guide will cover all aspects of Baidu SEO, providing you with everything you need to rocket your site to the top of the rankings and master the complex world of SEO in China. We’ll go deep into all of the unique considerations that must be kept in mind when optimizing for Baidu rather than Google.
Let’s begin with an introduction to Baidu SEO and how it’s different than Google.
This massive, in-depth guide will cover all aspects of Baidu SEO, including keyword research, technical SEO, link building, content marketing, social media, tools and analytics, and everything in-between
Chapters
Chapter 1
Chapter 2
Chapter 3
Chapter 4
Chapter 5
Chapter 6
Chapter 7
Chapter 8
Chapter 9
Chapter 10
![]()
While Google is the dominant search engine in most countries, only 2.3% of all searches in China happen on the Western search giant. This may be due in part to it being blocked by the Great Firewall in China, but even before the block was put in place, they never had a very strong position. Instead, local search engines rule in China.
Baidu is the clear leader in China, commanding 68.5% of the search market, with 360 Search a distant number two at 14.2%. Sohu’s Tencent-backed Sogou follows quickly behind at 12.4%. Alibaba’s relatively new mobile-only search engine, Shenma, has been growing rapidly with 1.6% overall, with a considerable larger presence on mobile search. Other search engines, such as Youdao, Bing, and Yahoo combined make up a measly 0.9% of all searches in China.
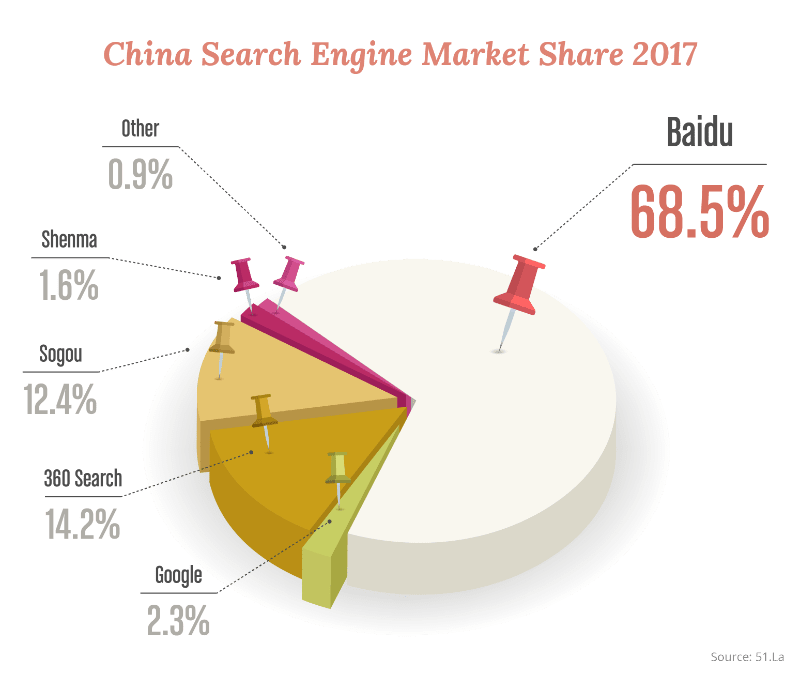
Source: 51.la
Founded by Robin Li and Eric Xu in 2000, Baidu is a technology company most well-known for their search engine. They were an early mover in China search, copying many aspects of Google in its approach and design. While it’s easy to dismiss Baidu as merely the Chinese Google clone, they remain very unique under the surface.
One of the main reasons Baidu has dominated the market is their ability to parse and interpret Chinese text more effectively than other search engines (such as Google), leading to higher-quality results.
The search engine has the biggest index of Chinese web pages in the world, and indeed is entirely Chinese-focused. The user interface is only available in Simplified Chinese, and gives much higher priority to Chinese language sites. Very few non-Chinese language sites are even included in the index or returned in search engine results.
Baidu, like Google does not restrict itself only to search, but offers a myriad of services including cloud computing, travel sites, maps, music and video platforms, translation services, a Wikipedia clone with over 13 million articles, a web browser, an Android-based mobile operating system, and even self-driving cars. Similar to Google, Baidu makes the vast majority of its revenue by selling ads on its search result pages and ad network.

Baidu, like Google does not restrict itself only to search, but offers a myriad of services including cloud computing, travel sites, maps, music and video platforms, translation services, a Wikipedia clone with over 13 million articles, a web browser, an Android-based mobile operating system, and even self-driving cars.
At its beginning, the similarities between Google and Baidu were clear. However, over the years, Baidu has added many unique features to their search engine result pages (SERPs). In the example SERPs below, you can see how Baidu is using different types of rich snippets to enhance the user experience. But before we dive into how Baidu and Google SERPs are different, it’s worthwhile to understand how they are similar and tend to influence each other’s SERP layout.
Here are 2 examples:

The interface is only offered in Simplified Chinese. No other languages are supported.
Links clicked on the SERP open in a new window, keeping the Baidu window always open for users to come back to it.
The majority of organic results have thumbnail images associated with them. Image-based related searches are present for almost every single search on the right side.
Often times it is very hard to distinguish between organic and paid results, even more so than Google. The Wei Zexi Scandal is one of the most well-known consequences of this.
Baidu’s own properties can occupy up to 70% of real estate on page 1. Rich Snippets on Baidu can also be much dynamic and interactive than on Google. Their size can be very tall, can have dozens of links in them, or even contain interactive JavaScript apps right on the SERP. While many of the rich snippets are from Baidu’s own properties, some can be applied for by any site using the Baidu Open platform, while others are paid promotional deals only available to a select few partner sites. Baidu’s usage on rich snippets been a major challenge for China SEOs.
Read our in-depth article about rich snippets in Baidu to learn more
Google uses structured data from schema.org markup and crawled data for rich snippets, while Baidu provides their own platform (Baidu Open or Baidu Webmaster Tools) for submitting structured data. Most of the rich snippets on Baidu are custom-designed for Baidu’s own properties and manually submitted by website owners.
Google’s mobile search shares the same URL as its desktop version. Baidu uses m.baidu.com for its mobile search engine.
Learn more about Baidu Mobile SEO here.
If your site is not mobile friendly, your site may be transcoded by Baidu to make it load faster for mobile devices. When this happens, your content will be hosted on Baidu’s servers. This all happens automatically without any action or approval by site owners.
Read our Baidu Mobile SEO to learn more
Baidu uses a domain credibility system that displays the level of trust it has for a domain in their SERP snippet. Sites must apply specifically for the badge for a fee, and is generally only available for paid search customers. The effect this badge has on organic ranking is unclear. Many believe Baidu does not treat it as a ranking factor, but it can definitely improve your website’s search appearance and click-through rate. In the snippet below, the site has a “V3” Baidu Trust rating.

The layout of the SERP can vary dramatically depending on the type of search. While some queries may display the traditional 10 blue links, most Baidu searches return a large number of ads, Baidu’s own properties, and other types of rich snippets.
Large enterprises have a relatively high degree of control for their own brand terms. Sites can apply for open widgets, submit their business address to allow their location to show up as a local result, create an enterprise page on Baike, or purchase special Brand Zone ads that take up the entire area above the fold.
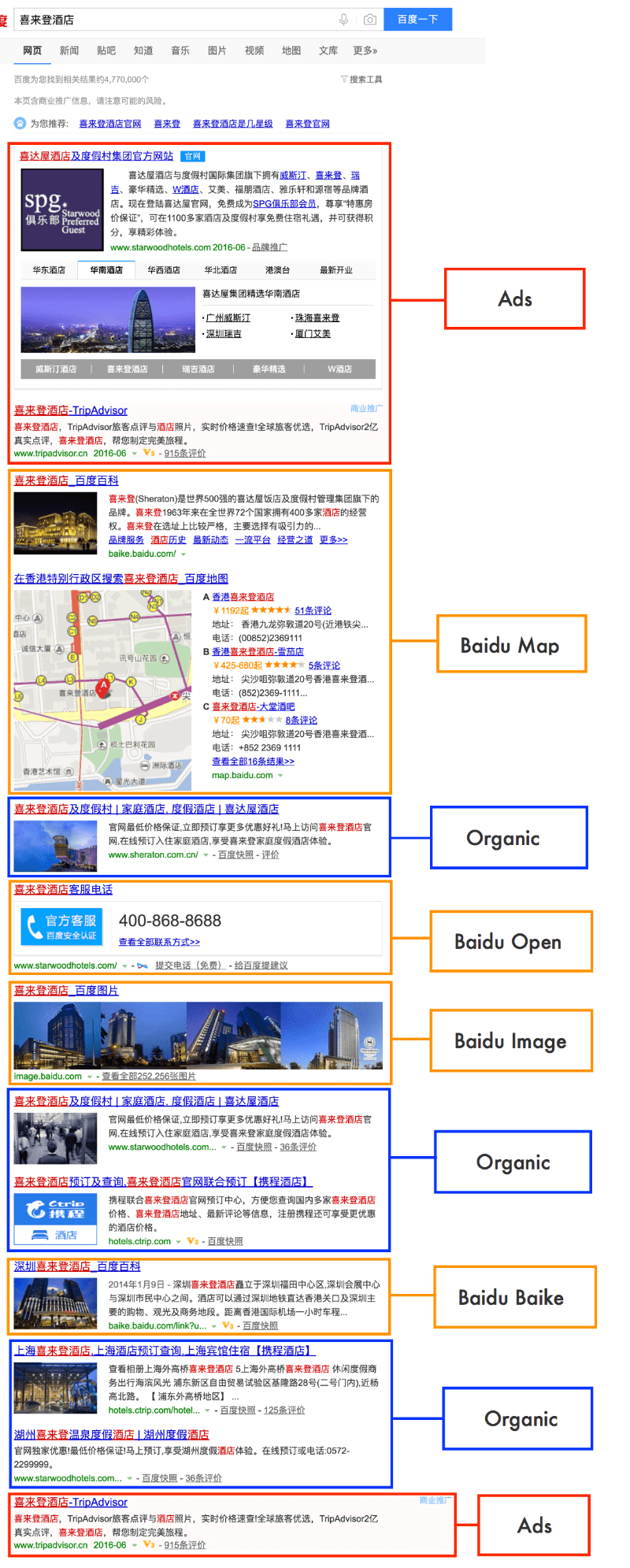
For informational queries, you can often see Zhidao, Jingyan or other industry-specific Baidu products such as Baidu Travel for travel-related queries.
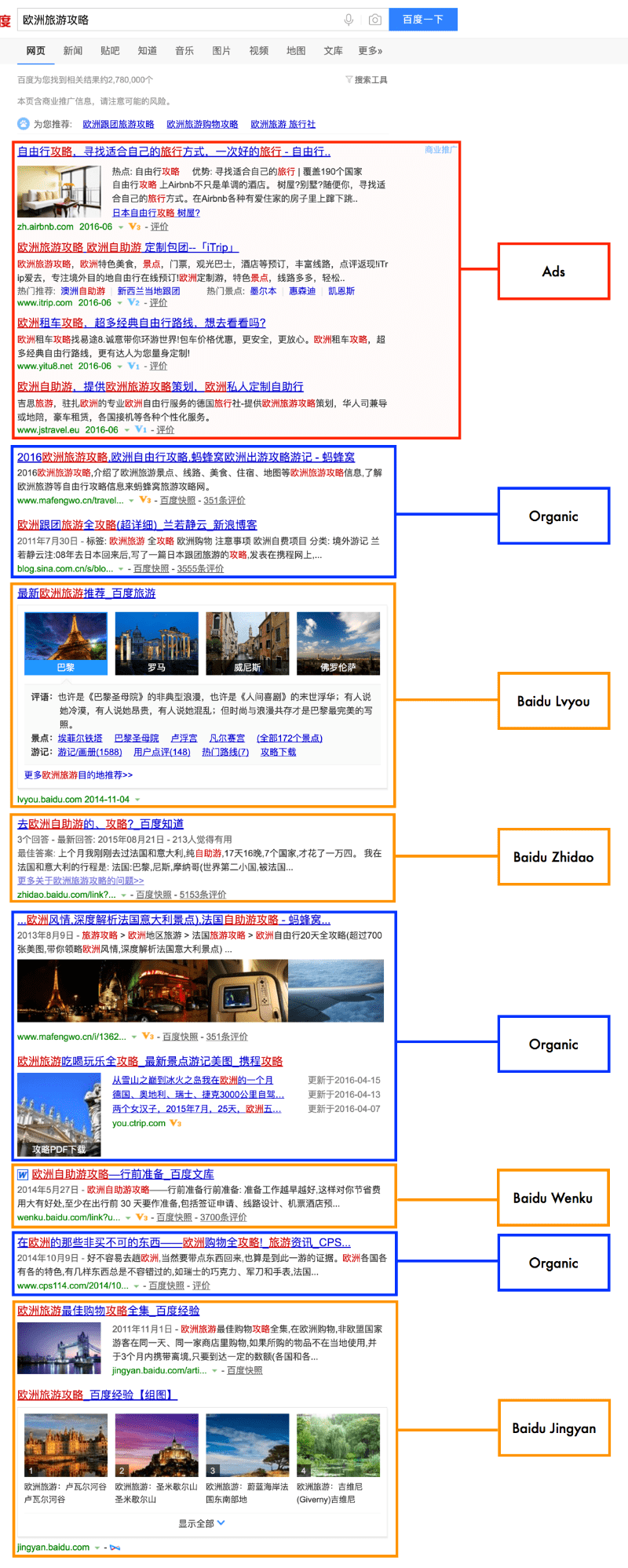
For China-based local of direction queries, you may see local results with navigation information. You may also see Zhidao results if directions are available there as well.
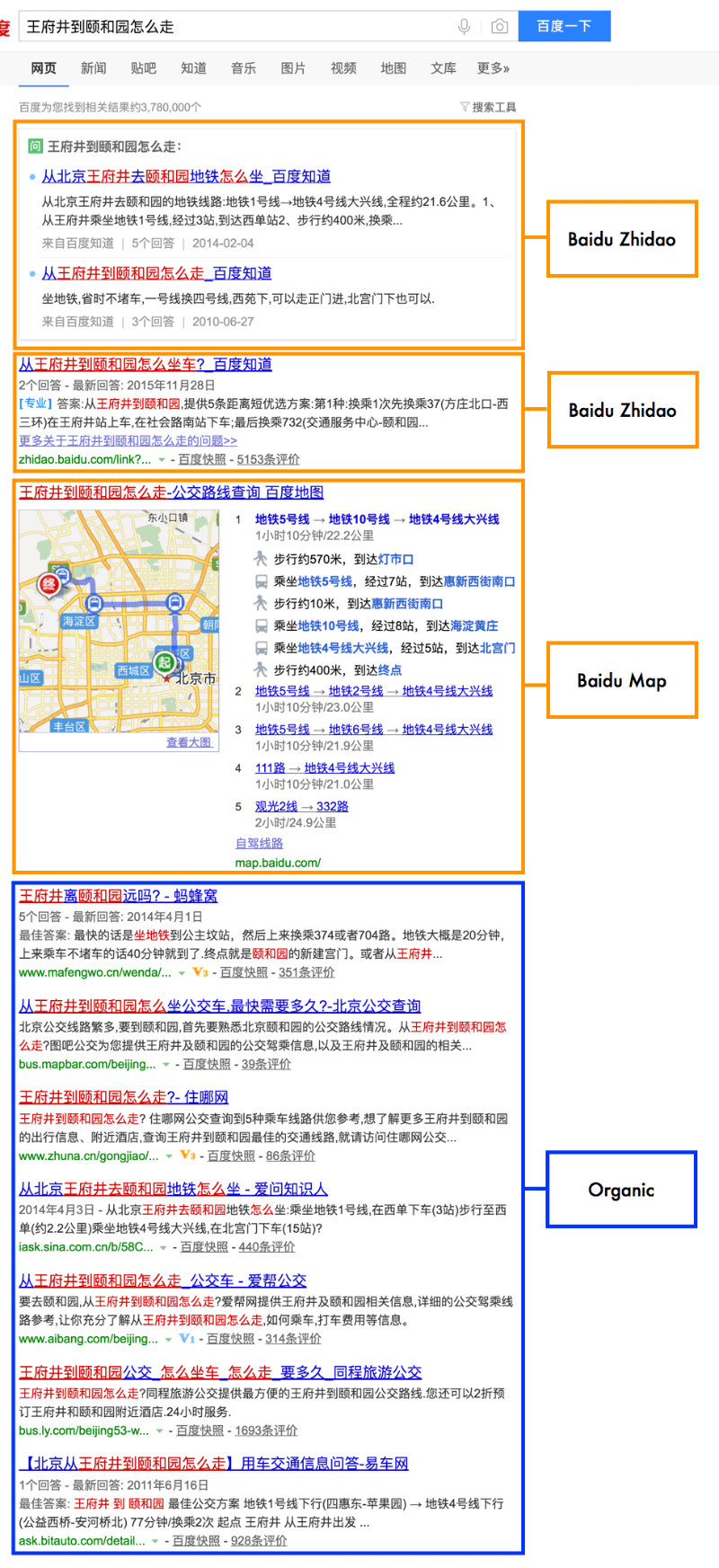
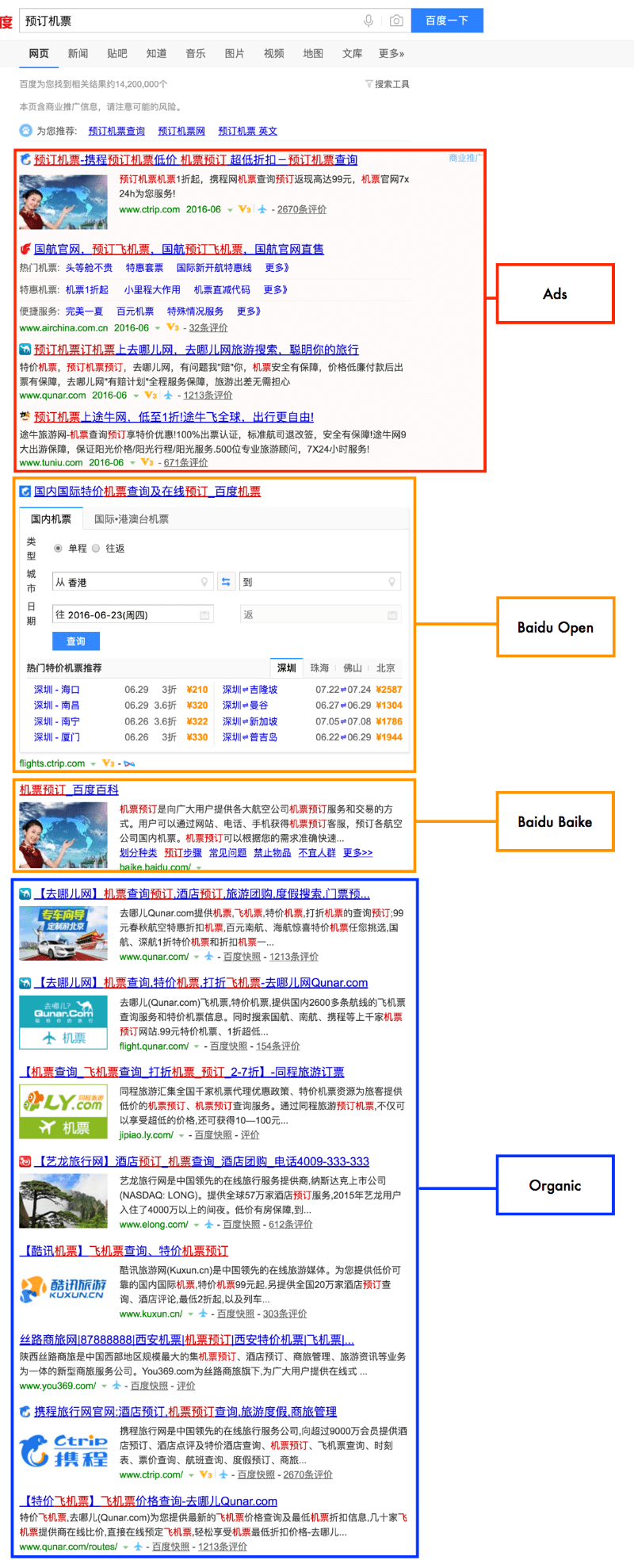
Transactional queries are probably the most similar to a typical Google result, since it is not always easy to create rich snippets that allow people to convert directly on the SERPs. For the search term “预订机票” (book plane tickets) you will get a rich snippet that allow you to choose flight information and get prices. But for most other industries, there will be fewer Baidu properties than other types of queries.
Though a great oversimplification, the easiest way to understand Baidu’s algorithm is that it abides by most of the same theoretical principles as Google’s, but is less effective in executing them in practice. So in a way, you can think of Baidu’s Algorithm as Google’s Algorithm with a 5-year lag.
For example:
While this simplification is true for a baseline understanding of some of the differences between Google and Baidu’s algorithm, there’s much more to it than this. Here is a summary of some of these differences based on our experience and extensive research:
Baidu is first and foremost a Chinese search engine. There is a massive explicit bias towards anything Chinese in Baidu’s algorithm. Whether it’s server location, content language, top-level domain (.cn), business address, backlinks, mentions, or citations — just about everything will be better for Baidu SEO if it’s from China or in Simplified Chinese.
Baidu’s crawling and indexation of non-Chinese language sites is much less reliable as well — they may be crawled slowly, less frequently, less deeply, or potentially not at all. Similarly, it is very rare to see a non-Chinese site to rank for Chinese language queries.
Baidu does this for several reasons, but the biggest is simply user experience. The majority of Baidu users are residents of Mainland China, interested in local content in Simplified Chinese.
Likewise, one reason why foreign sites not hosted in China have difficulty ranking on Baidu is that connections and speeds to overseas servers from Mainland China can be very unreliable due to the Great Firewall. Baidu has an incentive to deliver results that load quickly and reliably for their users, so locally hosted content will often prevail.

By focusing on just one language, Baidu has gotten very sophisticated in parsing and understanding Chinese content. Baidu has a strong advantage over Google in Chinese natural language processing, and typically provides more accurate results than any other search engine for Chinese queries.
Based on our experience, Baidu has much less tolerance for duplicate content. If a site is penalized by Baidu for duplicate content, it can take much longer to rebuild lost rankings. However, duplicate content remains a huge problem for Baidu, since content scraping is still a very common tactic for SEOs in China.
In recent years, Google has made substantial improvements in crawling JavaScript and AJAX content, but Baidu is still struggling. Generally speaking, it’s best to avoid these elements for major content areas of your site if you want to rank well on Baidu.
Baidu’s spider typically crawls Chinese sites much more frequently than Google’s. While crawl frequency depends on your website’s authority and update frequency, you can actually adjust Baidu’s crawl rate of your sites with Baidu Webmaster Tools. Learn more in our Baidu Webmaster Tools Guide.
Baidu values backlinks from China-based websites much more highly than foreign sites. When link building for Baidu, you should always aim for backlinks from sites hosted in China, written in Simplified Chinese, with Simplified Chinese anchor text.
In determining link quality, Baidu still lags far behind Google’s capabilities. While Google has gotten very good at spotting link spam, Baidu is still susceptible to old-school link spam tactics. With these black hat tactics still effective, they are unfortunately still used by many China SEOs.
Unlike Google, which uses advanced image recognition technology to provide relevant image results, Baidu still lags in machine learning for image processing. Therefore, correctly optimizing an image’s alt text and plain text content around the image is crucial to ranking well in Baidu’s image results.
Google’s system of handling penalties is much more robust than Baidu’s. In Google Search Console, website owners can view information about a site’s penalization and manual action status. They will typically process reconsideration request much quicker as well. In Baidu, one penalization can often mean the death of the domain, as it can take years to recover lost rankings. Some speculate that this may be why negative SEO tends to be a relatively more common tactic in Baidu.
Baidu favors websites that update content frequently. This is especially true for new websites. Just by frequently updating content very early on, sites may see improvement of overall rankings. Websites that aren’t updated for a few months may see a drop in rankings. We recommend publishing at least 1 piece of content each month, and to make sure you’ve submitted all of your website’s URLs to Baidu (learn how here). Content freshness still matters for Google, but to a lower degree than Baidu.
Baidu gives more weight to a domain’s age than Google does. Generally speaking, it’s more difficult to rank well for a new site and much easier over time.
For 99% of sites, the biggest organic competitor will be Baidu. That’s because for almost all search queries, you can see at least one Baidu property ranking in the top 5 positions. This by itself make SEO on Baidu very different than in Google.
Many suspect Baidu directly manipulates their algorithm to favor their own properties. While this may seem obvious at first glance, it’s possible that Baidu’s claim that it does not favor its own properties is true. In the early days of the Chinese internet when there was far less high quality content on the web, Baidu invested heavily in creating its own content hubs which quickly became very popular and attracted many backlinks. So it’s possible that Baidu’s dominance in organic search could be the result of deliberate manipulation, or simply that Baidu’s properties have accumulated so much content and links that they are now just impossible to beat.
It’s long been known that Google ignores the meta keywords tag, and only uses the meta description for SERP snippets. However, Baidu may still use meta keywords as a ranking signal. There is also some evidence that supports the possibility that meta descriptions may even affect rankings on Baidu, in addition to being used for the SERP snippet. This may come as a surprise to many, as these areas are easily manipulated for spammy tactics. While the weight given to this area may not be very big, it can still be a determining factor of whether the page will rank for the target keywords.
One of the most unique things about Baidu is the way they integrate their own products into their search results pages. This integration can sometimes be helpful for searchers, but it also makes SEO in China a unique challenge. Lets look at some of the most important Baidu properties that every China SEOs should be aware of:
Baidu News is the most popular news aggregation platform in China, curating content from over 1,000 news sources. Similar to Google News, Baidu News doesn’t publish it’s own content — all the news is aggregated by Baidu and will redirect users to the publisher’s website when clicked on. To get your content on Baidu News, you’ll have to be a verified news source, which has stringent criteria and is very difficult for foreign sites to pass. Interestingly enough, the application for Baidu News can be done through Baidu Webmaster Tools.
Check out Baidu’s article on news sources to learn more (Chinese)
Importance to Baidu SEO: Since content aggregated on Baidu News can also appear in organic results, it can have a huge impact on organic traffic. If your site meets the qualifications to be verified as a Baidu News source, you should absolutely do so.

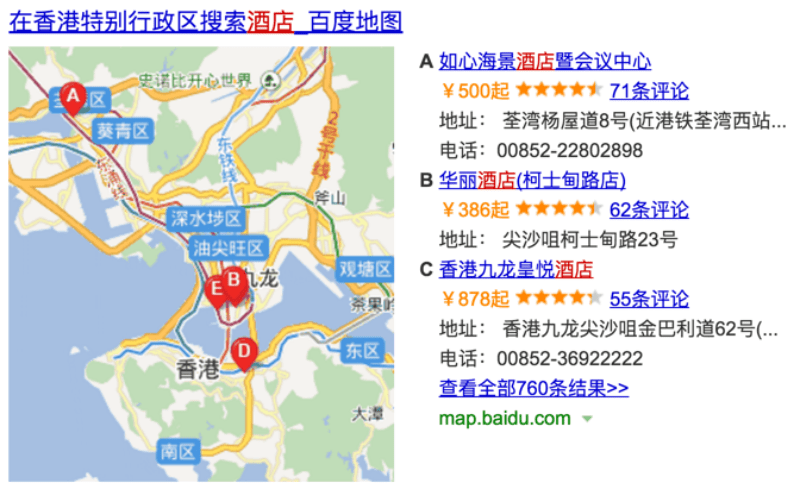
Baidu Maps is the most popular online map service in China. The entire globe is not covered, however — outside of Mainland China, only a few APAC regions such as Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, Korea, Japan, Thailand and Singapore are included. Although Baidu Maps does not offer as many features as Google Maps, the integrity and accuracy of Baidu Maps in China is by far the best you can find in the country.
Importance to Baidu SEO: When searching for navigational queries or local business’ information on Baidu, you will usually see Baidu Maps snippets in the SERPs. Unfortunately, local SEO on Baidu is not as effective as on Google, since local listings will not link back to their main website, only their Baidu maps profile.
Baidu Images has the biggest index of web images from Chinese websites in the world. Although not as powerful as Google Images in many aspects, their preference in indexing Chinese content still allows them to provide useful results when searching for Chinese keywords or China-related topics.
Importance to Baidu SEO: Optimizing for Baidu Images can be a very effective strategy to gain organic traffic. While most Baidu properties will not link out to 3rd party websites, Baidu Images is one of the very few exceptions. Ranking in Baidu Images can bring direct organic traffic to webpages. They appear very frequently on SERPs, and ranking in Baidu Images is relatively easy, so if your site own many high-quality images, Baidu Images should be a part of your SEO strategy.

Baidu Tieba is a network of communities / forums created and maintained by Baidu, and is one of the largest sites of its kind on the internet. Tieba’s seamless integration with Baidu’s search engine has allowed tens of thousands of niche forums and communities to flourish in just one platform. No matter how obscure your keyword search may be, you can almost always see a Tieba discussion dedicated to that particular topic to help searchers connect with users of similar interests.
Importance to Baidu SEO: Due to its prevalence on Baidu SERPs, Tieba a great place for SEOs to build their own content, as it’s often easier to rank highly for their Tieba discussion than their own site.

Baidu Wenku is the biggest online Chinese document sharing platform in the world. You can find educational materials, research papers, business documents, law documents, novels, comics, and much more. The concept of Wenku is kind of similar to Slideshare, but Wenku supports a larger variety of document formats. To promote content creation, Wenku utilizes a credit system where users must use credits to download documents. Credits can only be earned by uploading popular content or by purchasing them directly. In recent years, Wenku has also developed itself as a self-publishing platform where authors can promote and sell their content.
Importance to Baidu SEO: Uploading content on Baidu Wenku is a commonly-used SEO tactic in China. This is especially true for high value products or B2B solutions when potential clients are looking for more in-depth information to make their purchase decision.

Baidu Baike is China’s answer to Wikipedia, providing (theoretically) unbiased articles on every imaginable subject that anyone can edit. With over 16 million articles, Baike has far more content than the Chinese version of Wikipedia, and has played a huge role in educating the population in China. One interesting distinction is that while Baike theoretically aims at providing unbiased content, they are still a much more commercially inclined platform than Wikipedia. Enterprises can pay for increased control of their brand’s Baike page — quite a difference from the non-profit, freedom of information philosophy of Wikipedia.
Importance to Baidu SEO: Maintaining a corporate page on Baidu Baike can be helpful for optimizing for branded search queries. Since Baike is considered as the authoritative source of information, building positive, unbiased content on your company’s Baike page can be extremely important.

Baidu Zhidao is one of the most popular Q&A platforms in China. Think of it as the Chinese Yahoo Answers. Baidu Zhidao’s provides helpful answers to millions of questions with a smooth user experience.
Importance to Baidu SEO: Marketing on Zhidao is excellent for building highly targeted traffic to your website. Although Zhidao can’t bring you direct organic traffic, since questions on Zhidao tend to rank so highly, answering questions related to your business can help educate potential customers about your offerings. In fact, this such an effective marketing tactic that some internet marketing experts in China specialize solely on Zhidao optimization.
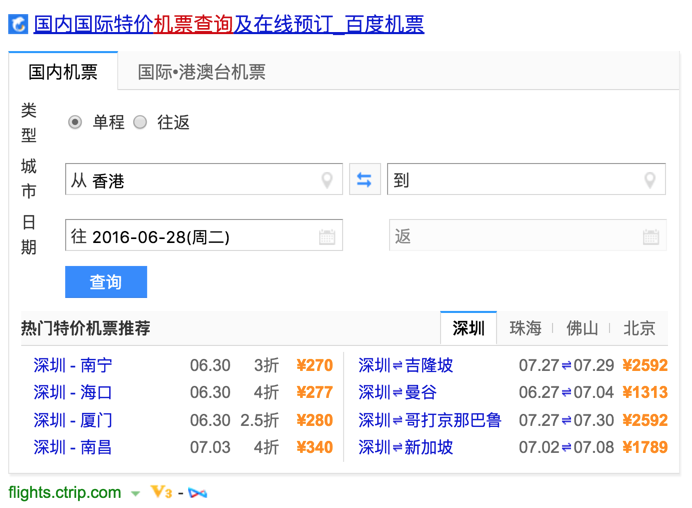
Unlike the Baidu products above, Baidu Open is not a product or website in itself. Rather it’s a platform that allows developers to create their own SERP widgets with structured data. Unlike Google or Bing, Baidu doesn’t support schema.org markup for rich snippets. Sites can only rely on Baidu Open, Baidu Webmaster Tools, or for Baidu to algorithmically feature their content.
Unfortunately, only a very limited number of rich snippets formats can be applied for via Baidu Webmaster Tools. Many more customized widgets that appear on Baidu SERPs are made through special partnership deals with Baidu, and are only available for a small number of sites.
Learn more about Baidu rich snippets and submit structured data through Baidu Webmaster Tools
Importance to Baidu SEO: As this is Baidu’s official platform for submitting structured data, every Baidu SEO should be familiar with it in order to understand what kind of rich snippets their websites are eligible for.
The products mentioned above are the ones that appear most commonly on Baidu SERPs. However, there are several dozen more that may also appear for select queries. Here’s a few more worth mentioning:
Baidu Jingyan (literally “experience”) is a focuses on providing step-by-step answers to informational queries
A group buying service provided by Baidu. When searching for products or services listed on Baidu Nuomi (often location-based), Nuomi’s rich snippets may appear on the SERP
A travel guide and review platform created by Baidu. The Lvyou rich snippet will often appear for travel-related search queries
A new service launched last year that aggregates product information from China e-commerce sites. Baidu Mall represents Baidu’s most recent attempt to crack the e-commerce market in China — before Mall, Baidu also tried with products such as Hui, Weigou, Temai, and others. So far, it’s not been enough to wrestle much market share away from current market leaders JD.com, or Alibaba’s Tmall and Taobao.
Check out our full gallery of 100+ Baidu properties and rich snippets
Baidu and Google seem very similar on the surface, but the deeper you go, the more the differences emerge. Baidu has more features and more ads crammed into their SERPs, with deep integration with their own products, but their algorithm is simpler than Google’s in terms of determining page quality, and has a strong preference for everything Chinese.
While Baidu still follows Google in many ways, this may not be the case for much longer. With the development of machine learning being integrated into search engine algorithms, each will develop independently. As machine learning picks up on local user behavior and search intent, cultural and behavioral differences of Chinese users will diverge Baidu even further from Google.
Chapter 2 : Keyword Research
![]()
Chapters
Chapter 1
Chapter 2
Chapter 3
Chapter 4
Chapter 5
Chapter 6
Chapter 7
Chapter 8
Chapter 9
Chapter 10