![]()
Technical SEO is all about making it easier for search engine spiders to crawl and index your site’s content. Typical areas of focus for technical SEO include site speed, stability, crawler directives, site architecture, code structure, design, compatibility, and security.
The goal of on-page optimization is to make it easier for search engines to understand what each page on the site is about, which will help rank the page for relevant content. This typically means structuring your content in an easy-to-digest way, and using keywords and appropriate content in key areas of the page.
Luckily, technical SEO and On-Page Optimization for Baidu share some similarities with Google. If your site has already been optimized for Google, you’re part of the way towards optimizing your site for Baidu, but there’s still a number of additional considerations to keep in mind.
In this chapter, we’ll cover all of these additional factors, along with our tips and recommendations for optimizing your content for Baidu. In order to concentrate fully on insights for Baidu SEO, we’re going to skip the basics of general-purpose technical SEO and on-page optimization. If you’re looking for some good resources to learn or brush up on the basics, here are some of our favorites:
Step-by-Step “Technical SEO” Checklist from Webris
Technical Site Audit Checklist from Moz
On-Page SEO: Anatomy of a Perfectly Optimized Page from Backlinko
Since Baidu targets a primarily Mainland Chinese audience, they typically give preferential treatment to almost everything Chinese. This includes the hosting location of your web servers.
To get the best SEO performance on Baidu, you’ll want to host your site within Mainland China (Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan unfortunately do not count). That’s not to say that sites hosted outside of China will always rank poorly, but local hosting is certainly an advantage.
There are two primarily reasons for this preferential treatment. The first is that hosting in Mainland China is a strong signal that the site is targeting the local Chinese market. The second is due to the Great Firewall. Many sites outside of Mainland China, and thus outside the Great Firewall, load much more slowly than domestic sites, and may not always be reachable. As Baidu is tasked with returning sites in their search results that are fast and reliable to local users, this puts foreign sites at a great disadvantage.
Unfortunately, due to local laws, hosting a website in China is far more complicated than in other countries. In this section we will discuss some most important considerations of hosting to Baidu SEO, to help you assess whether having a China based hosting environment is feasible for your China SEO projects.
If you want to host websites in China, you will need an Internet Content Provider (ICP) License, there are two types:
There are extra requirements you’ll need in order to get approval from the government, such as a local physical addresses, phone number etc.
For details on how to obtain an ICP license, TutsPlus has a great guide
The ICP license number is typically listed in the footer of every website hosted in China. These numbers can be looked up in the Chinese government’s portal for more information about the license holder.

Baidu has never mentioned ICP licenses in SEO publications, so there’s no sure way to know if having an ICP license is a ranking factor in Baidu. However, we believe that an ICP license will indirectly help a website on Baidu in the long run. The main reasons are:
.cn is the country code top level domain (ccTLD) of China. Based on our experience, Baidu will not give .cn domains ranking priority. In fact, the usage of .cn domains isn’t even necessarily a popular choice for local companies either (look at Baidu**_._com**). However, when it’s feasible, we still recommend using the .cn domain instead of a subfolder or subdomain. Here’s why:
Getting a .cn domain only requires a Chinese ID, which is considerably easier than hosting in China or getting an ICP license. However hosting in China and obtaining a ICP license will have a much higher value for SEO than a .cn domain.

The Great Firewall of China (GFW) is a blanket term used to describe internet censorship in China. Sites that publish politically sensitive content, self-publishing platforms such as social media sites hosted outside of China, or content deemed inappropriate by the Chinese government (gambling, pornography, etc.) are typically blocked in China by the Great Firewall. Many of the top sites in the world, such as Google, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, YouTube, Wikipedia (in Chinese), and The New York Times are all inaccessible everywhere in Mainland China.
Even foreign sites with no political or controversial topics are not fully safe from the Great Firewall. All sites hosted outside of China may be slow to reach or intermittently inaccessible at times. This can vary based on the time of the year, with more disruptions near politically sensitive events in China. In 2014, an entire CDN was blocked in China, making thousands of innocent websites inaccessible.
Before doing any China SEO for any foreign websites, it’s a good idea to check if the site is blocked in China.
GreatFire.org Analyzer is a very useful tool to check if a website’s been blocked in China.
greatfirewallofchina.org doesn’t provide as much information as GreatFire.org, but can still be useful for reference.

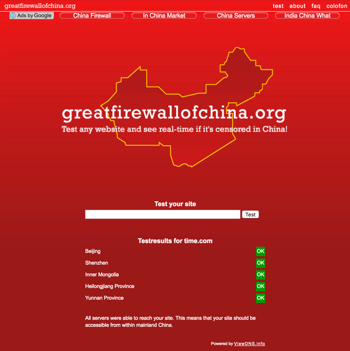
China is a big country. Sites can be inaccessible or slow in some parts of the country, while perfectly fine in others. After verifying accessibility, we recommend testing site speed in multiple regions throughout China. Here are a few free tools you can use to test server speed from different cities in China:
(The above tools are only available in Chinese)
If your site loads slowly in China, leveraging a content delivery network (CDN) could be a good solution. However, the cost and complexity of setting up CDN in China are relatively high compared to other options. If you are willing to invest in setting up a business and doing SEO in China for the long run, this could be a useful option.
Selecting a good CDN provider is extremely important. Below are 3 main categories of China CDN services, their benefits, and the most popular vendors within each category.
A local CDN is ideal if you are looking to set up a dedicated CDN service for users in China only. This type of CDN services usually have the best performance in China. The most popular China based CDN providers are:
Global CDN providers that provide good coverage in China may work well for websites that need a global CDN network that cover more than just China. However, do keep in mind that the Chinese government can decide to block a global CDN without warning or cause. Unless you are convinced the CDN is really too big to fail, it may be better to stay with local CDN providers.
Some of the most popular ones are:
In recent years, tech giants in China started providing local CDN services as well. These CDN services are more affordable, but are mostly self-service which means that you will have in-house IT expertise in China to set up and maintain them.
China Hosting References
The adoption rate of HTTPS is much slower in China than in the US or UK. It wasn’t until 2015 when Baidu finally announced their full support in crawling and indexing HTTPS sites. Later, in summer 2016, they announced an updated crawler with improved abilities in handling HTTPS.
Similar to Google, Baidu claims to give HTTPS websites a small ranking boost. However, at this stage we still think Baidu’s support of HTTPS is still not mature enough for webmasters to make the switch, as the risks still outweigh the potential benefits.
The recommendations listed above are all good practices that website owners should follow as much as possible. However, in reality various constraints may prevent you from implementing some or all of them. All is not lost — here are some alternative solutions if the options listed above are unavailable.
If you are not able to host your website in China, you may want to consider hosting in Hong Kong, Japan, or Singapore. With good internet infrastructure and a relatively close proximity to China, sites hosted here may load much faster for Chinese users than other international regions. If Asia is not an option at all, the US West coast is a much better option than US East coast or Europe.
Getting a .cn domain is easier than hosting your website in China, but if you still can’t get one, using a gTLD (Generic Top Level Domains) with a subdomain (e.g. http://cn.example.com) should still work fine. Even a subdirectory (e.g. http://www.example.com/cn), though not as good as other options, will still be acceptable.
Here are a few common mistakes international websites often make when trying to target China:
Although many search engine crawlers have gotten better in crawling JavaScript, Baidu is much less likely to process JavaScript than Google. In fact, in Baidu’s own SEO College, the search engines says they do not process any content in JavaScript. Therefore, implementing any site content in JavaScript for Baidu is absolutely not recommended. This includes AJAX content, JavaScript links, language switchers in JavaScript, or anything else that hides content or links in JavaScript.
It’s a common practice to load popular Javascript libraries like jQuery or Bootstrap from a CDN hosted by Google or other large companies in the West to leverage browser caching and improve site speed. However, very often these CDNs can be blocked or throttled in China, and will cause your site to load slowly, incorrectly, or not at all — simply for using a single hosted file.
To avoid this issue, we highly recommend loading common libraries from a CDN hosted in China. They’re frequently used, so site visitors may already have them cached in their browser. You can also be sure they will not be blocked or slow down your site.
Even if you aren’t able to host your entire website in China, referencing hosted JavaScript / CSS libraries in China for your Chinese website will remove a common point of failure and improve your site speed in China. Here are a few popular hosted libraries in China:
Please keep in mind that the opposite issue may occur if you share one code base between your China site and other locations. If a user outside of China tries to load the site that loads libraries from a China CDN, it may load much more slowly for them. If possible, try to load libraries from a CDN hosted closest to where each user is.
While it’s a disappointing to see this remain an issue in 2017, URL parameters can unfortunately cause trouble for Baidu’s crawlers quite easily. This is especially true if there are multiple URL parameters in the URL structure.
Similarly, using URL parameters to differentiate languages such as http://www.example.com/?lang=cn is perhaps the absolute worst way you can structure a multilingual site — this is even true for search engines that have few problems with URL parameters in general.
Using a country code top level domain (such as .sg, for Singapore) in conjunction with a China subdomain or subdirectory (such as china.example.sg or example.sg/china) will be confusing to both users and search engines to ascertain which region this site is targeting. If possible, use a generic top level domain (gTLD) such as .com instead of using a subdirectory or subdomain.
Placing sharing widgets for China-censored social networks like Facebook, Twitter, YouTube etc. in your China website is not a good idea, since they will be blocked by the Great Firewall, and will hurt your site speed. Instead, we recommend using China-based social sharing plugins like Baidu Share, which will be more appropriate for local users anyways.
The chart below illustrates the benefits to China SEO compared to the resources required to implement them.

A well-designed information architecture serves 3 goals:
The general principles of good information architecture for Google also applies for Baidu. It’s important to understand that in many cases, Baidu’s crawler is still less tolerant and less sophisticated than Google’s, so more care should be placed on this step than for a Google-optimized site.
Like most things in life, a good balance is important. If a site is too flat, the user experience may suffer, due to the overwhelming number of links on each page. However, a site that is too deep may create challenges for Baidu’s crawler, which can have trouble crawling very deep sites. Our advice is to structure your site to be only as deep as it needs to be to optimize the user experience.
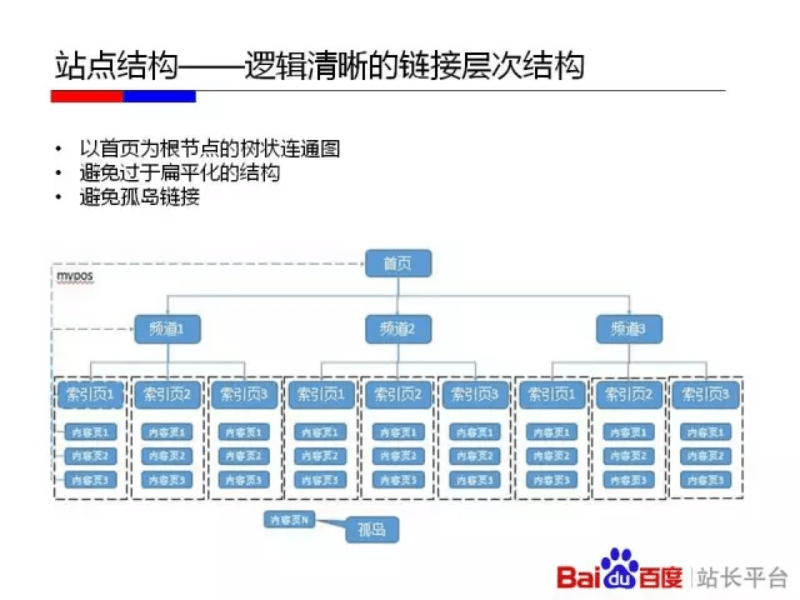
Image source: Baidu Webmaster Tools Official Site
Mobile search is redefining the shape of search engines. Google is shifting to a mobile first index, and Baidu has been placing a higher priority on its mobile search engine than desktop as well.
Check out our Baidu Mobile SEO Guide to learn more about this topic
Recently Baidu has launched their own version of Accelerate Mobile Pages (AMP), which is designed to provide a better user experience for mobile searchers with extremely fast landing pages. Since AMP is typically hosted on Google, Baidu needed its own alternative. Although its impact to Baidu SEO is still minimal and difficult to tell how MIP will evolve over time, it’s still worth noting.
Learn more about Baidu MIP on the Dragon Metrics blog
Baidu Webmaster Tools offers useful tools for crawl testing and monitoring. The Crawl Error Tool will show any server or crawling errors they’ve experienced on your site. You can also fetch your site as Baidu to see how Baidu Spider sees your site using the Crawl Diagnostic Tool.
Learn more in our Baidu Webmaster Tools Guide
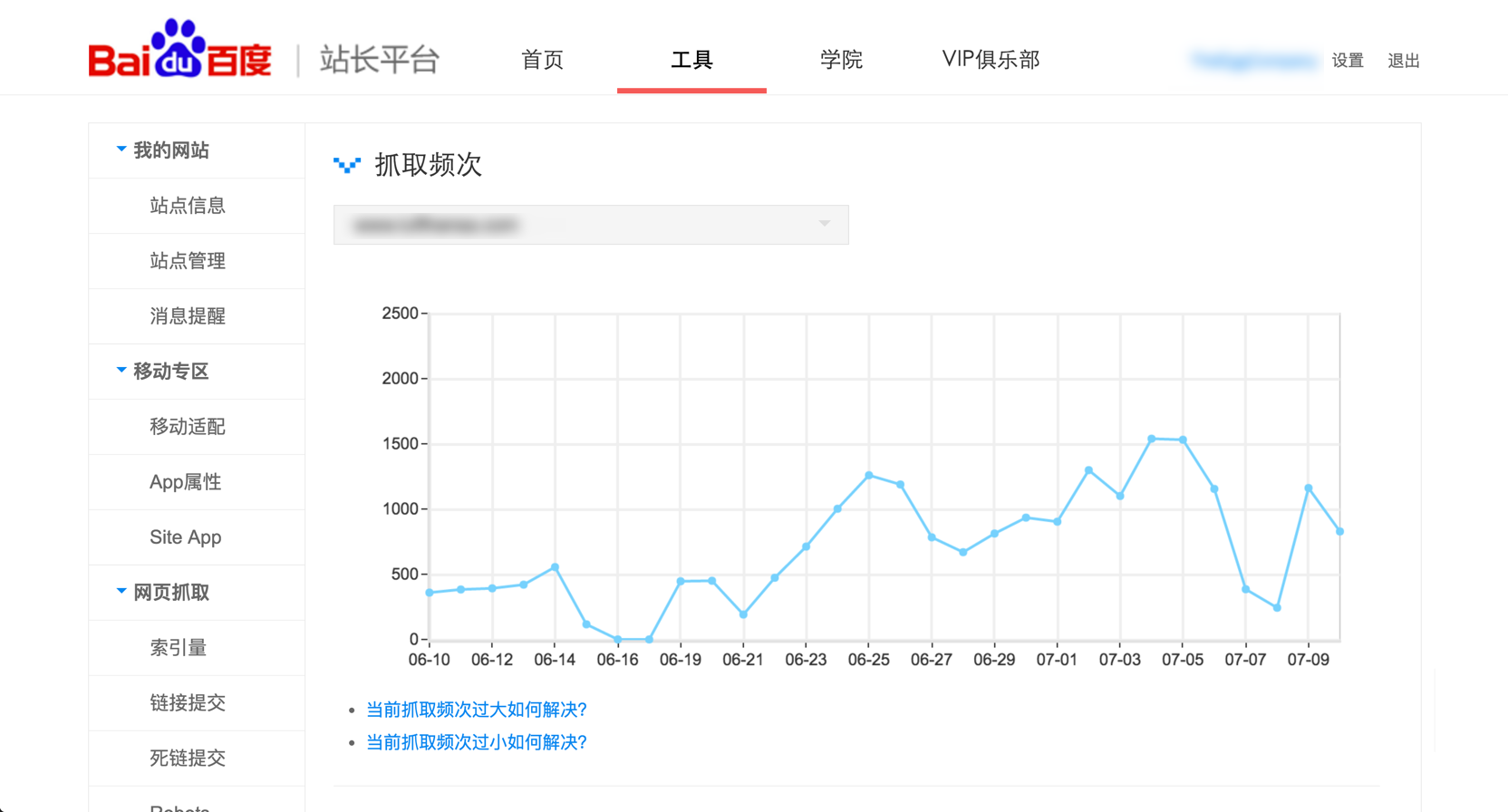
Another more technical way to monitor if Baidu’s spiders can crawl your site normally is to look at your website’s server logs. To do so, you’ll need be able to identify Baidu’s crawler. Both Desktop and Mobile uses the user agent token baiduspider, but with a different full user agent string.
Mozilla/5.0 (Linux;u;Android 4.2.2;zh-cn;) AppleWebKit/534.46 (KHTML,like Gecko) Version/5.1 Mobile Safari/10600.6.3 (compatible; Baiduspider/2.0; +http://www.baidu.com/search/spider.html)
Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; Baiduspider/2.0; +http://www.baidu.com/search/spider.html)
Here is an article about log file analysis for SEO
Baidu’s crawler reacts differently than Google when they encounter broken links or links with excessive redirects. They heavily rely on internal anchor text to understand context of a page. We’ve seen big improvements in Baidu indexation and rankings just by optimizing a site’s internal linking.
If there are too many redirects in a chain, search engines will usually give up following them at some point and never reach the final destination page. This means that the page will not be crawled or indexed by the search engine
Statuses in the 400-499 range are all types of client errors, which means the problem has to do with the client’s request, not the server’s response. There are a number of different types of errors in this range, but the vast majority of them are 404 errors, which means nothing is located at the specified URL.
This issue means that there are no outbound links found on the page. This poses a user experience issue and represents a lost internal linking opportunity.
There are multiple ways Baidu uses to discover URLs on your website. To ensure maximum indexation, we should make sure we’ve setup everything properly. Fortunately all of these will be fairly easy with a modern CMS.
Optimize Sitemaps for Baidu
A sitemap is a file that contains many or all of the URLs on a site, with metadata about its modified date, change frequency, and priority. A properly set up sitemap can help search engines find all pages on your website and understand your site structure, especially for sites with many URLs. The sitemap format for Baidu is nearly identical to Google, so if you already have a sitemap that is properly formatted for Google (which most modern CMS can generate automatically), you don’t have to worry about tweaking your sitemaps too much for Baidu. Here are a 2 main differences in sitemap handling between Baidu and Google.
Baidu has a unique tag they will use to identify whether an URL is designed for desktop, mobile or both devices.
<mobile:mobile/> // Mobile pages
<mobile:mobile type=”mobile”/> // Mobile pages
<mobile:mobile type=”pc,mobile”/> // Responsive pages
<mobile:mobile type=”htmladapt”/> // Dynamically served pages
Here’s an example of sitemap entry for a mobile page:
<url>
<loc>m.example.com/mobile.html</loc>
<mobile:mobile type=”mobile”/> // This is the tag for mobile page
<lastmod>2009-12-14</lastmod>
<changefreq>daily</changefreq>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url>
Learn more about Baidu Mobile SEO with our extensive guide
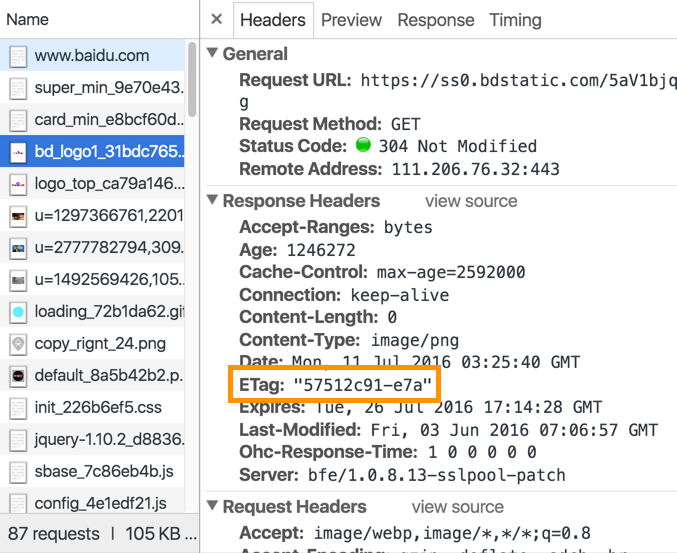
eTag is a part of HTTP protocol that are used to inform clients if the page has changed since last visit. With eTag-enabled websites, clients won’t have to make requests to website resources if their pages haven’t changed, thus saving bandwidth and resources on both the server side and client side. Baidu officially endorses the usage of eTag for websites and will crawl sitemaps more frequently for websites who have it enabled.
Here’s a quick overview of implementing eTag for websites
Just like for Google, it’s often useful for webmasters to submit their sitemaps to Baidu via Baidu Webmaster Tools.

Learn more about submitting sitemaps to Baidu
Besides sitemaps, there are 2 other unique methods Baidu provides to allow webmasters to submit their new URLs to Baidu quickly.
Real-time Active Push allows you to programmatically submit URLs to Baidu. This is by far the quickest method webmasters can use to ensure indexation. However, this method requires developing your own tools to communicate with Baidu’s server.
Real-time Active Push is a fairly new development, but Baidu have been pushing it very hard. The main reason behind the push is due to the prevalence of content scraping and stealing original content in China. To ensure your site gets credit for its original content, using Real-time Active Push to allow Baidu to instantly index your content is recommended. We would encourage every Baidu SEO engaged in content marketing to consider using this method.
To implement Auto Push, you just simply have to inject a simple piece of JavaScript code into your website’s section. With this code snippet on the page, every time someone visits the URL that piece of code will be triggered and the URL will be submitted to Baidu.
Learn more about both Real-time Active Push and Auto Push methods in our Guide to Baidu Webmaster Tools
The optimal setup to ensure quickest and highest indexation is to implement all three methods together — sitemaps, Real-time Active Push and Auto Push. All site owners can submit a sitemap. In addition, use Auto Push if you have rights to edit the website’s HTML code, and use Real-time Active Push if you have developers that can create the necessary tools.
As Baidu ranking algorithms are not as advanced as Google, following old school on-page SEO best practices can still yield good results. It’s still important to take care using target keywords and their variants naturally in page content, and not engaging in keyword stuffing.
Learn how to utilize on-page keywords for maximum SEO benefits in this infographic from Backlinko
Optimizing keyword placement within your content will most likely need to be done by native Chinese writers.
Learn more in our section about content marketing in China
Although browsers and search engines support using Chinese characters in URLs and even domain names, it’s still not a recommended practice. They may be difficult to type, read, or pronounce for many users, and often times will be displayed as percent encoded, which is not human-readable. In our experience, Baidu doesn’t consider keywords included in the URL as a ranking factor at all.
So if we’re not using Chinese characters in our URLs, what’s the best way of writing them? Two other options are frequently used: Pinyin or English translations. Pinyin is the standard method of writing Mandarin Chinese using latin characters, and is understood by most Chinese people. For example, the word, “products” in Chinese is “产品”, which can be written as “chanpin” in Pinyin. Therefore, the URL for the products page could be written as example.com/chanpin. Another popular method is to simply use the English translation for the URL, e.g. example.com/products.
Our research has shown that Baidu does have the ability to correctly interpret pinyin as Chinese characters, so this could potentially allow Baidu to understand the content on the page based on the URL. In the screenshot below, we can see Baidu correctly guessing the Chinese characters for a pinyin query. The text at the top of the page asks the user “Are these the Chinese characters you meant to search for?”
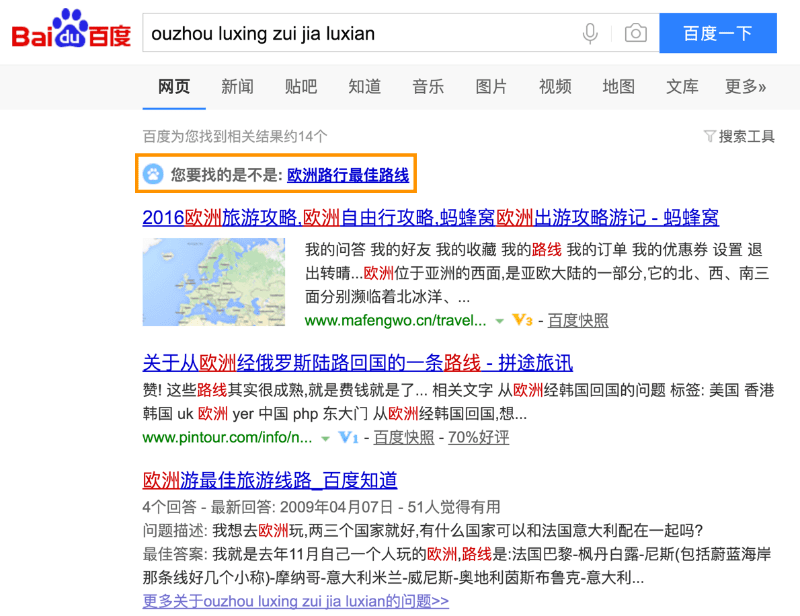
However, in recent years, we’ve seen many of the most authoritative sites in China use English for URLs instead of pinyin. There may not be a clear winner on which is best for SEO, but the trend amongst the largest sites in China is moving towards English URLs. Pinyin should also be fine, but Chinese characters should be avoided.
Optimizing search appearance for higher CTR has became more important in the world of Google recent years, as more research has found it may have an impact on rankings. But what about Baidu?
It’s widely believed that Baidu uses CTRs of the top 20 search results to determine the rankings of a specific query. Because of this, using automatic clicking software to artificially increase CTRs was a very common tactic for black hat SEOs in China. It was not until recently that Baidu made progress in identifying this kind of spam. To optimize your web pages for the best CTR as possible, here are a few guidelines:
Below is a good example of properly formatted organic search snippet:


One of the most unique features of Baidu SERPs is their frequent usage of rich snippets. Unlike Google, which uses schema.org markup and crawled data, Baidu has their own platform for submitting structured data. This makes getting included in SERP features on Baidu completely different than on Google.
Check out our guide to getting rich snippets or glossary of Baidu rich snippets to learn more
There are plenty of tools out there for optimizing your technical and on-page SEO. We’re going to walk through how to use Dragon Metrics for optimizing your site, but most other tools have similar features. Feel free to explore and use any tool you prefer — the important thing is that you use some sort of software to automate the process. Doing technical SEO manually is time-consuming and error-prone, and is not recommended.
The Site Auditor feature in Dragon Metrics will crawl your site just like a search engine, and look for over 50 common technical and on-page SEO issues. Just a short time after the crawl begins, all findings and step-by-step recommendations will be presented in a report similar to what you’d receive from a professional SEO agency.
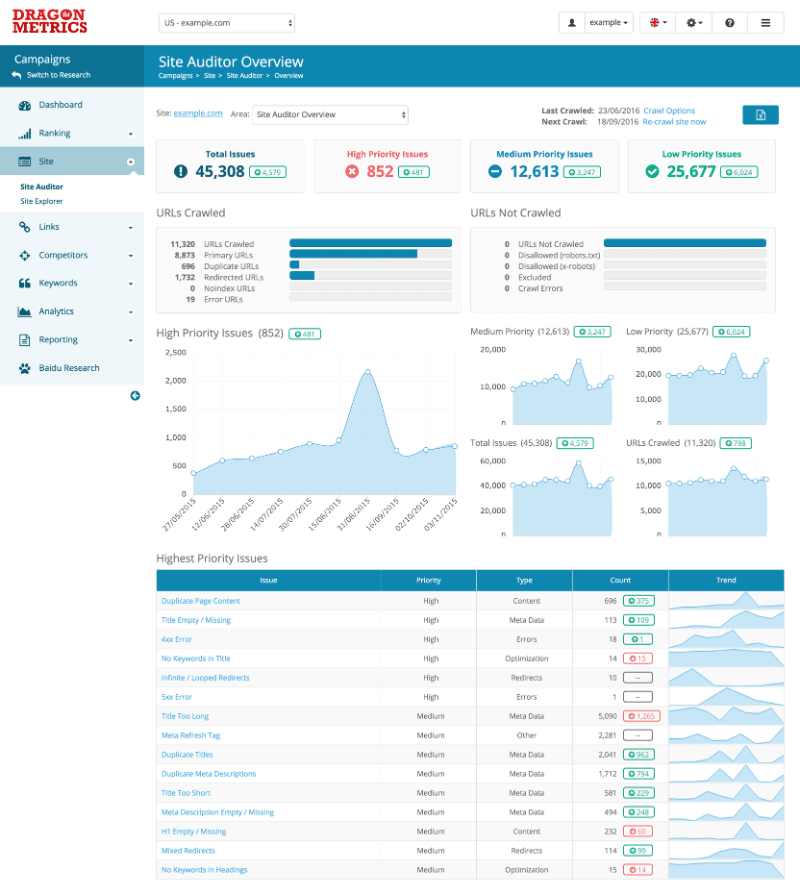
Common SEO issues such as broken links, duplicate content, redirection problems, dead-end pages, missing / duplicate / un-optimized title or meta tags, and many other issues will be automatically reported by Dragon Metrics. Each issue is tracked over time, and comes with detailed step-by-step instructions and recommendations on how to fix each one.
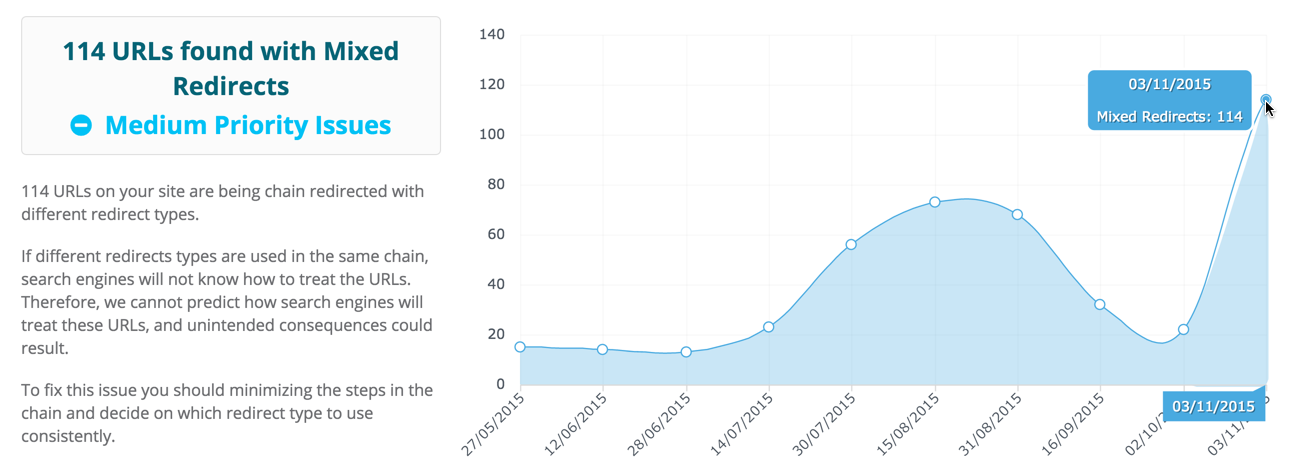
Each URL affected by the issue is listed along with any other data or details you need to fix it.
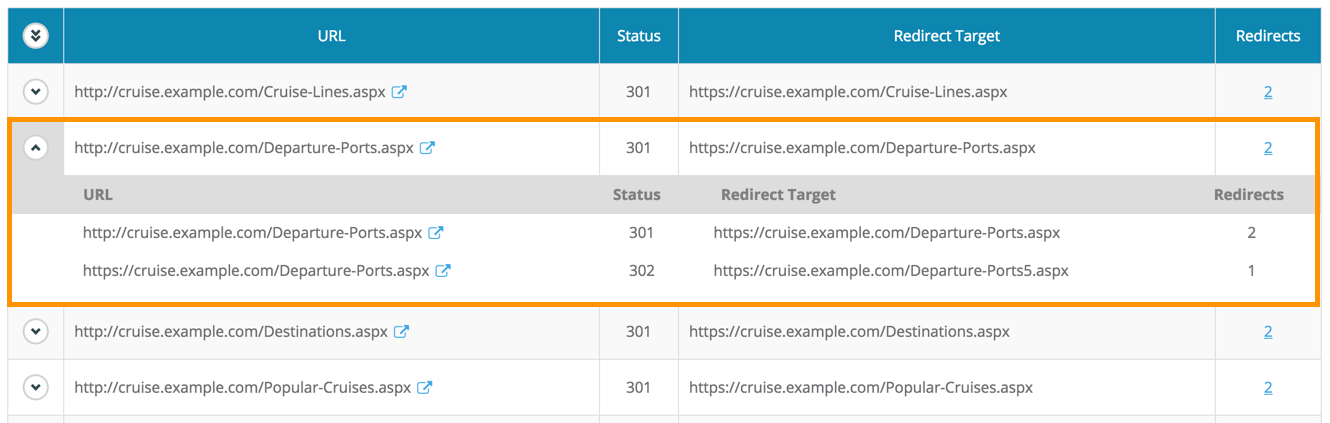
Since Dragon Metrics’ crawler will spider your site the same way search engines do, you can identify crawl issues before Baidu does. Crawl errors are displayed in an easy-to-visualize summary, with detailed analyses available for each one.

A summary of optimization issues are displayed at the bottom of the Site Auditor page.
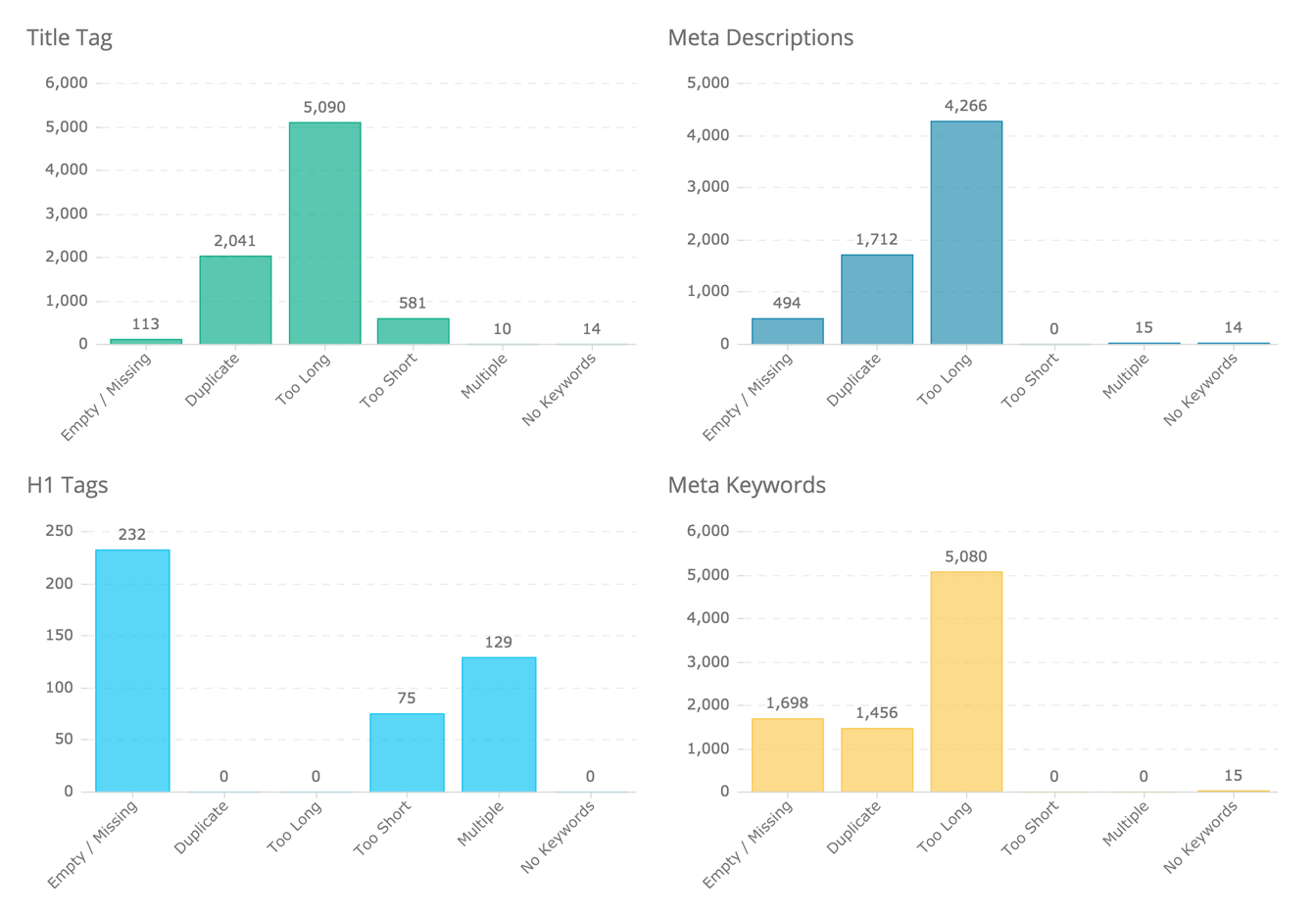
All data can be exported to an Excel spreadsheet or included on a customizable white-labeled online or PDF report.

It’s clear there are many additional technical considerations for Baidu SEO in addition to the normal optimizations typically made for Google. Generally speaking, we believe technical and on-page SEO are more important for Baidu SEO than for Google for two main reasons:
Although many of these recommendations can be difficult to implement, they can be the difference between success and failure of your SEO campaign in China.
Chapter 4 : Content Marketing
![]()
Chapters
Chapter 1
Chapter 2
Chapter 3
Chapter 4
Chapter 5
Chapter 6
Chapter 7
Chapter 8
Chapter 9
Chapter 10